5. Data Sources¶
TIM’s database contains documents that are the underlying data for the visualisations in TIM. These documents are organized into groups, so that they can be searched together.
There are currently two groups of documents available in TIM Open Access.
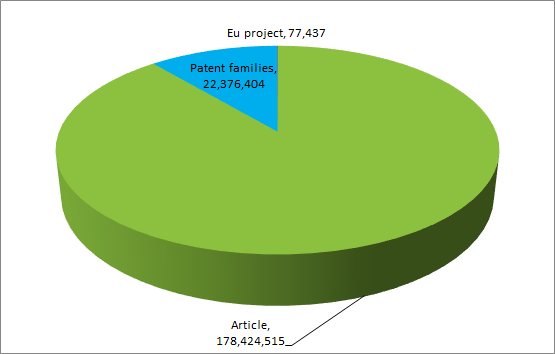
The main group, which consists of three types of documents: Scientific publications, Patents and Granted EU projects.
The COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19), which consists of COVID-19 and coronavirus-related documents.
These groups don’t communicate with each other, i.e. searches that the User does can be done on either, but not on both at the same time.
More than 200 million documents are currently indexed in TIM Open Access’ database, including scientific articles from Semantic Scholar, Patents from Patstat and EU projects from Cordis.
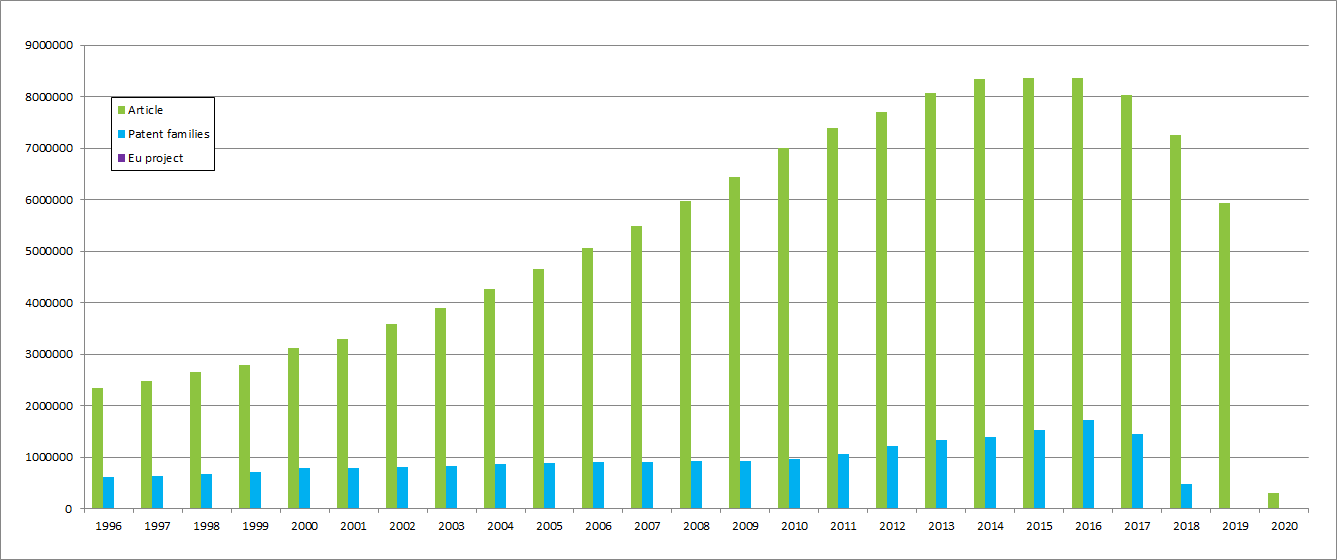
The coverage per year is not homogeneous for each type of data. The coverage in TIM depends on what is available at the time of retrieving the data from the providers.
The distribution of documents is as follows from 1996 (existing data before but not represented in the graph).
5.1. Scientific publications¶
The database in TIM Open Access contains documents from the Semantic Scholar database.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered search and discovery tool that helps researchers discover and understand scientific literature that’s most relevant to their work. Semantic Scholar uses machine learning techniques to extract meaning and identify connections from within papers, then surfaces these insights to help scholars gain an in-depth understanding quickly. A variety of carefully tuned mechanisms are used to make sure only high-quality academic papers are indexed.
Semantic Scholar sources its data from a number of scientific journals and databases, the current corpus includes research publications in all fields of science. This is a complete list at the time of writing: ACL, ACM, AMiner, ArXiv, BioOne, CiteSeer, Clinical Trials Transformation Initiative, DBLP, De Gruyter, Frontiers, HighWire Press, Hyper Articles en Ligne (HAL), IEEE, Karger, Microsoft Academic, MIT Press, OdySci Academic, Papers with Code, Project MUSE, PubMed, SAGE Publishers, Science, SciTePress, SPIE, Springer Nature, Taylor & Francis, The Royal Society, Wolters Kluwer.
From wikipedia:
Semantic Scholar is a project developed at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence. Publicly released in November 2015, it is designed to be an AI-backed search engine for scientific journal articles. The project uses a combination of machine learning, natural language processing, and machine vision to add a layer of semantic analysis to the traditional methods of citation analysis, and to extract relevant figures, entities, and venues from papers. In comparison to Google Scholar and PubMed, Semantic Scholar is designed to highlight the most important and influential papers, and to identify the connections between them.
5.2. Patents¶
The patent documents are extracted from the database PATSTAT from the European Patent Office. It contains patents from more than 90 patent authorities including all the major countries. We consider all patent documents in Patstat with priority date from 1996 onwards. The patent documents are then grouped per patent family when at least one of the members of the family is in English. The underlying assumption is that one patent family equals one invention.
A significant lag in the patent data can be observed in Patstat for the three last years (see graph above). The reason for this lag can be explained at least by three reasons: 1. Patent documents are published 18 months after their application 2. Cleaning and processing the data coming from other authorities than EPO 3. The EPO database is released two times a year.
The Setis team at JRC calculated PATSTAT data coverage and estimates for future versions.
JRC estimates that this coverage is approximately of: 10% for y-1; 40% for y-2; 70% for y-3; and only reaches almost 100% for y-4. For more information see below.
5.3. Granted EU projects¶
This dataset contains projects funded by the European Union under the fifth framework programme for research and technological development (FP5) from 1998 to 2002, FP6 from 2002 to 2006, FP7 from 2007 to 2013 and the Horizon 2020 framework programme for research and innovation (H2020) from 2014 to date. Grant information is provided for each project, including reference, title, starting date, programmes, participant countries, subjects and objectives. This data is extracted from the Cordis dataset, accessible on the European Union Open Data Portal.
5.4. COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19)¶
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic and with the view to boost research, the Allen Institute for AI together with other leading research groups is collecting and making available for free the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19). For more information, see here.
This dataset can only be searched separately from the other groups of documents.
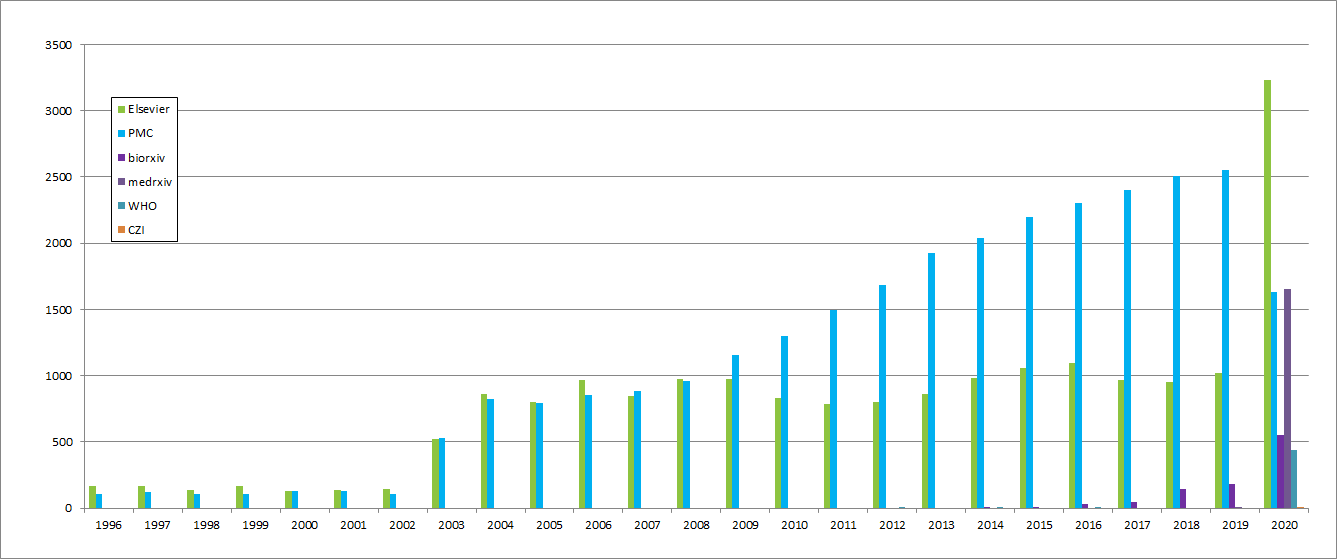
This dataset contains, at the time of writing, more than 57,000 publications on COVID-19 and coronavirus research (e.g. SARS, MERS, etc.), from the following sources:
PubMed’s PMC open-access corpus
Additional COVID-19 research articles from a corpus maintained by WHO
bioRxiv and medRxiv pre-prints using the same query as PMC
The documents are refreshed on a weekly basis, and so these numbers may have changed substantially since the time of writing. The distribution of documents follows (documents from before 1996 are not represented on the graph):